The if Statement
What is if Statement in Java ?
The if statement is a conditional control flow statement in Java that allows you to execute a block of code only when a given condition is true.
It is used to implement decision-making in programs — the code inside the if block is executed only if specified condition evaluates to true.
Key Points:
- if is used for simple condition checks.
- Only the code inside the block runs if the condition is true.
- There is no alternative action if the condition is false — the program simply skips the block.
- The condition must return a boolean (true or false).
- Logical operators (&&, ||, !) and relational operators (==, >, <, >=, <=) are commonly used inside if conditions.
- You can have multiple if statements in the same program:
- They can be back-to-back or have gaps between them.
- Each one will be checked independently.
Syntax:
if (condition) {
// code to run if condition is true
}- condition must be a boolean expression (returns true or false)
- If the condition is true → execute the block
- If false → skip the block
Flow diagram for the following examples:
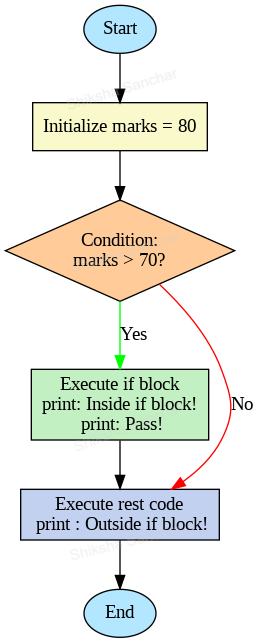
Understanding this diagram:
This flowchart represents the flow of a Java program that checks whether marks > 70 using an if statement.
- Start: The program begins execution.
- Initialize: A variable marks is assigned a value (e.g., 80).
- Condition Check: The program evaluates the condition marks >
70.
- If the condition is true, it enters the if block and executes:
System.out.println("Inside if block!");System.out.println("Pass!");
- If the condition is false, the if block is skipped.
- If the condition is true, it enters the if block and executes:
- Execute Rest Code: After the if block (or skipping it), the program
executes:
System.out.println("Outside if block!");
- End: The program finishes execution.
This flow ensures that the if block is only executed when the condition is true, while the remaining code executes regardless of the condition.
Example 1:
class ShikshaSanchar {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int marks = 80;
if (marks > 70) {
System.out.println("Inside if block!");
System.out.println("Pass!");
}
System.out.println("Outside if block!");
}
}Output of the Program:
Inside if block!
Pass!
Outside if block!
Explanation:
This program demonstrates the use of a simple if conditional statement in Java.
- A variable marks is initialized with the value 80.
- The program then uses an if statement to check whether the condition marks > 70 is true.
- Since marks = 80, and 80 > 70 is true, the condition is satisfied.
- As a result, the statements inside the if block are executed:
- “Inside if block!”
- “Pass!”
- After the if block, there's another System.out.println which is outside the if block, so it executes regardless of whether the condition was true or false.
Example 2:
class ShikshaSanchar {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int marks = 20;
if (marks > 70) {
System.out.println("Inside if block!");
System.out.println("Pass!");
}
System.out.println("Outside if block!");
}
}Output of the Program:
Outside if block!
Explanation:
- This program demonstrates the behavior of a simple if statement when the given condition is false.
- A variable marks is declared and initialized with the value 20.
- The if statement checks the condition marks > 70 → which becomes 20 > 70 → false.
- Since the condition is false:
- The statements inside the if block are completely skipped.
- No output from "Inside if block!" or "Pass!" is printed.
- The program continues execution after the if block and prints:
- “Outside if block!”
Summary:
The if statement allows conditional execution of code. It runs a block only if the given condition is true.
- Used for simple decision-making.
- If condition is true → code runs.
- If condition is false → block is skipped.
- Rest of the code runs regardless.